
Domain names are essential for any online business or organization. They are the web addresses that customers and clients use to access websites, and they are also the foundation of a company’s online brand.
As such, it is essential to protect domain names from cyber threats that can compromise the security and integrity of a website.
In this article, we will provide an overview of the different types of cyber threats that can affect domain names and offer practical tips on how to protect your domain name from cyber threats.
By following the advice in this article, you can rest assured that your domain name remains secure and that your website and online brand are protected from cybercriminals.
Common Cyber Threats to Domain Names
Cyber threats pose significant consequences, such as damaged reputation, data theft, and financial loss for any business. In this section, we will discuss some of the most common cyber threats to your domain name and how to protect your business from them.
Domain Hijacking
Domain hijacking occurs when an unauthorized person gains access to your domain name and takes control of it.
This unwelcome intrusion can occur through various methods, including:
- Social engineering
- Phishing attacks
- Exploiting vulnerabilities in your domain registrar’s security infrastructure
Once these bad actors gain control over your domain, they wield the power to redirect your website visitors to their own online territory.
This could potentially result in the theft of sensitive information or, in more distressing scenarios, demand money to give your domain back. Keeping your online territory safe from these sneaky moves is super important. We’ll show you how in the next sections.
DNS Spoofing and Cache Poisoning
DNS Spoofing and Cache Poisoning are methods used by online attackers to redirect web traffic. Imagine it as a way to make you visit the wrong place on the internet.
DNS Spoofing involves replacing the IP address of a legitimate website with that of a malicious one.
Cache Poisoning, on the other hand, involves corrupting the DNS cache of a server to redirect traffic to a malicious website.
Both of these techniques can lead you astray on the internet, potentially putting your data and privacy at risk.
Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks are a form of online trickery that you should be aware of. In these schemes, cybercriminals use fake emails or websites to pretend they’re trustworthy sources. Their goal? To get your sensitive information like usernames, passwords, or credit card numbers.
Phishing attacks can also target your domain registrar account, where you manage your domain name. If they succeed, they can take control of your domain.
Besides these three, there are other cyber threats and security challenges that you need to be vigilant about, including:
- Domain Squatting (Typosquatting): Malicious actors register domain names that are similar to popular websites, often with typos or misspellings, in an attempt to capture traffic from users who make typing errors in the web address. They may use these domains for malicious purposes or ad revenue.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks: DDoS attacks target domain names by overwhelming the associated web server with a massive volume of traffic, making the website unavailable to legitimate users.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks: Attackers intercept communication between users and a website by compromising DNS or other network components. This allows them to eavesdrop on sensitive information or modify data exchanged between the user and the website.
- Brute Force Attacks: Hackers attempt to guess the username and password of your domain registrar account or DNS management panel to gain control over your domain settings.
- Expired Domain Theft: When a domain name expires, it may become available for registration by anyone. Cybercriminals can monitor the expiration of valuable domains and snatch them up when they become available.
- Registrar Data Breaches: If your domain registrar experiences a data breach, your domain-related information could be exposed, making it easier for attackers to target your domain.
Best Practices for Protecting Your Domain Name
In a survey by IDC in 2021, they found that 87% of companies in North America, Europe, and Asia Pacific had faced DNS attacks. On average, each attack cost about $950,000.
This highlights the importance of protecting domain names from cyber threats to avoid significant financial losses and reputational damage.
Here are some best practices to follow:
-
Choose a Reputable Domain Registrar
Choosing a reputable domain registrar is the first step in protecting your domain name from cyber threats. Look for a registrar that has a good reputation for security and customer service. It’s important to read reviews and ratings before making a decision.
One of the most reliable domain registrars in the market is Shortdot.bond. The company has a proven track record of providing top-notch security and customer service to its clients. Some of the domains registered with Shortdot.bond include .bond, .cyou, .icu, and .sbs.

Button: [Register your premium domain name]
-
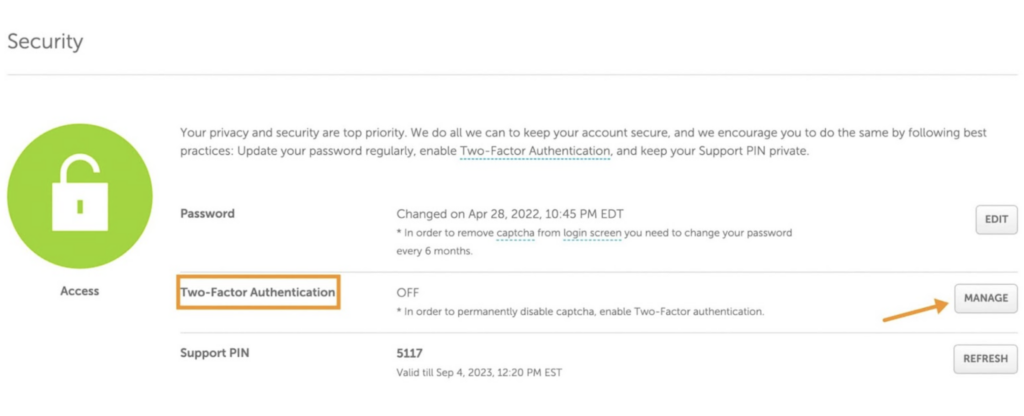
Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Protect Your Domain Name
This security feature makes your account safer. It asks for a special code, along with your password, to get into your account. So, even if someone gets your password, they can’t get in without the code. You can set up 2FA easily in your domain registrar’s account settings.
Having 2FA adds an extra layer of security and makes it much harder for hackers to access your domain name. It is an important step to better protect your online assets.
-
Use Strong Passwords
A good password is at least 12 characters. It should have upper and lower case letters, numbers, and symbols. This makes the password stronger.
Avoid using common words or phrases, and don’t reuse passwords across multiple accounts. It’s also important to change your password regularly and avoid sharing it with anyone.
- Enable Domain Locking
Domain locking stops your domain name from being transferred to another registrar without your permission. It prevents unauthorized transfers. When domain locking is enabled, your domain name cannot be transferred without your permission.
Even if a hacker gains access to your account, they won’t be able to transfer your domain name to another registrar without your explicit permission. You can simply enable domain locking through your domain registrar’s account settings.
-
Monitor Domain Expiry Dates

Protect Your Domain NameIf your domain name expires, it can be vulnerable to cybercriminals who may try to register it for themselves. To avoid this, it’s important to regularly monitor your domain expiry dates and ensure that your domain is renewed on time.
Set up automatic renewal if possible, and make sure that your payment information is up-to-date. This will help ensure that your domain name remains active and secure.
Advanced Security Measures
In addition to the basic security measures discussed earlier, there are advanced security measures that can be implemented to further protect your domain name from cyber threats.
Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC)
DNSSEC adds security to the Domain Name System (DNS). It uses digital signatures to protect DNS data. This ensures the DNS data is authentic and not tampered with and prevents attackers from redirecting your website’s traffic to malicious websites by spoofing DNS data.
Setting up DNSSEC involves working together with the domain registrar and DNS hosting provider. Not all registrars and hosting providers support DNSSEC, so it is important to check before implementing it.
Domain Name System Security Operations (DNS-OARC)
DNS-OARC is a non-profit organization that provides technical assistance and research to improve the security and stability of the DNS. They provide various tools and services to assist organizations in keeping an eye on and safeguarding their DNS infrastructure..
Using DNS-OARC tools and services can help you detect and mitigate DNS-based attacks, such as DNS amplification attacks and DNS cache poisoning attacks.
It is recommended to use DNS-OARC tools and services in conjunction with other security measures for a comprehensive approach to DNS security.
Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS)
1 / 1SSL/TLS is a security protocol that jumbles up data shared between a web server and a browser. This encryption protects sensitive stuff like your login info and credit card numbers, so hackers can’t sneak in and understand it. It makes sure your data stays safe when it moves between the server and your device.
Using SSL/TLS like RapidSSL certificate, for your website is crucial. It helps safeguard user information and builds trust with your site visitors.
Working closely with Cybersecurity Professionals
Hiring cybersecurity professionals can be a great way to protect your domain name from cyber threats. These professionals have the expertise and experience to help you identify and mitigate potential risks to your domain name.
There are many cybersecurity firms and professionals available, but it is important to choose the right one for your needs. When choosing a cybersecurity pro or company, some aspects to take into account include:
Expertise and experience: Look for professionals who have experience working with domain names and have a deep understanding of the latest cybersecurity threats and best practices.
Reputation: Do research on the cybersecurity person or company. Check that they have a good reputation and successful track record. This will ensure they are qualified.
Cost: Consider the cost of engaging a cybersecurity professional or firm, and ensure that it fits within your budget.
Once you have identified a cybersecurity professional or firm to work with, they can help you with a variety of tasks, including:
Domain name monitoring: Cybersecurity experts can watch over your domain name to catch any strange things happening, like unauthorized changes or someone trying to take control of your domain.
Cyber threat assessments: A cybersecurity professional can thoroughly assess your domain name and identify any vulnerabilities or potential risks.
Security audits: A security audit can help identify any weaknesses in your domain name security and provide recommendations for improvements.
Overall, hiring a cybersecurity expert or company can be a good way to keep your domain name safe from online threats. When you team up with a knowledgeable person in this area, you can be sure that your domain name stays secure and shielded from possible attacks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, protecting your domain name from cyber threats is essential for maintaining the security and reputation of your website.
By following the best practices outlined in this article, including choosing a reputable domain registrar, enabling two-factor authentication, using strong passwords, enabling domain locking, and monitoring domain expiry dates, you can significantly reduce the risk of cyber attacks.
1 / 1These easy and effective strategies can ensure your domain name stays safe and secure. This way, you can concentrate on expanding your online presence without worries.
Author Bio

Protect Your Domain Name

Millie Pham
Millie Pham serves as an SEO content marketer and an AI enthusiast at By Millie Pham, where she explores various marketing tactics and strategies. Millie also has a particular interest in leveraging artificial intelligence to boost growth for online businesses. Those looking to connect with her can reach Millie Pham at millie@bymilliepham.com.
