Are you tired of launching marketing campaigns that fail to generate clicks, sign-ups, or sales?
Chances are, your message is not landing because it is not aligned with what your audience is doing or looking for. But that can be fixed.
In this article, we will explore what behavioral targeting is and how to do it for your brand. You will also find the dos and don’ts to make sure you engage your target audience better.
By the end of your read, you will know how to craft campaigns that feel relevant, increase customer engagement, and drive more conversions.
Meet Your New Superpower: Behavioral Targeting In Action
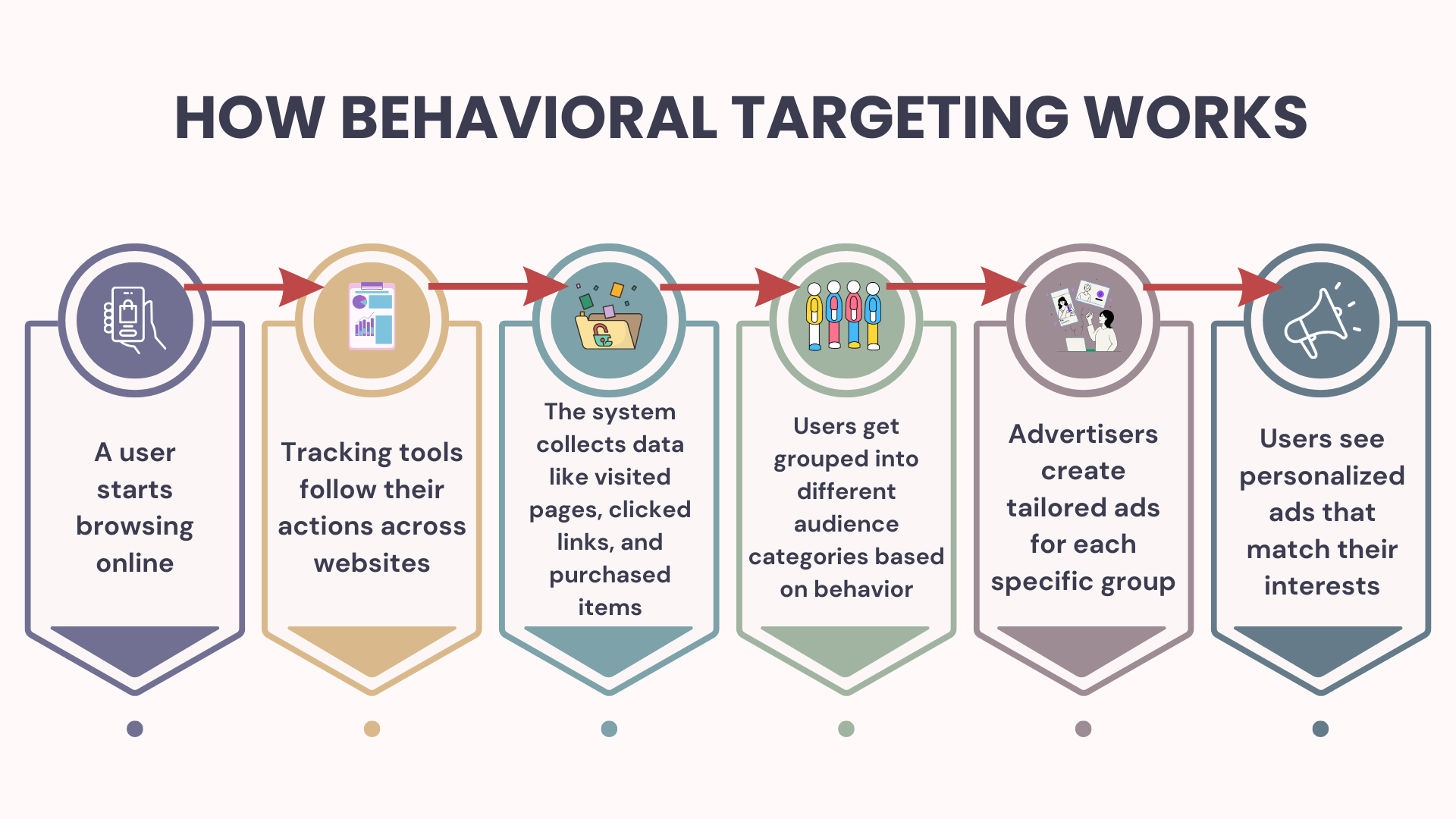
Behavioral targeting uses behavioral data to deliver personalized content based on how people interact online. Think clicks, purchases, time on page; real signals that reveal what your audience wants.
How does it work?
Behavioral tracking tools gather data collected from your brand’s websites, apps, and other digital touchpoints. Then, you group people into audience segments based on user behavior and serve relevant ads that match their interests.
For example, suppose you are in the B2B space selling these rapid prototyping materials for manufacturing companies. A prospect visits your site, explores your injection molding and vacuum casting services, then leaves without converting.
With behavioral targeting, you can retarget them later with targeted ads on LinkedIn or industry blogs your audience frequents. In your ad, you can feature fast lead times, material specs, or a free quote offer to bring them back at the right moment.
Unlike contextual targeting, which focuses on the content of the page, behavioral targeting focuses on the person: what they have done, not just what they are reading.
What do you gain from using this method?
- Improve your advertising campaigns with higher ROI.
- Increase customer engagement through more relevant content.
- Recover lost revenue with timely reminders for high-intent users.
- Cut acquisition costs through precise targeting of repeat visitors.
- Turn interest into action with ads that re-engage cart abandoners.
- Strengthen your integrated marketing campaigns with behavior-based insights to make every channel feel like part of the same conversation.
Now, let’s dive into the different types of behavioral targeting so you can use each one with purpose.

i. Onsite Behavioral Targeting
With this type, you can track how users interact with your web pages, from pages visited and time spent to search terms and even scroll depth. It relies on tracking pixels and browser cookies to gather behavior signals within your site.
Then, you can use the collected data to adjust the on-site experience. This can include:
- Showing targeted ads
- Recommending related products
- Highlighting sections based on users’ online behavior
Suppose a user visits your pricing page and then exits. Later, while browsing another section of your site, they see a targeted ad promoting a limited-time discount or free trial related to the same product.
These are all designed to guide users closer to a purchase. You can bring in a conversion rate optimization expert at this stage. They can help you analyze your data and make sure your website guides visitors to complete the actions that matter most, whether that is signing up, requesting a quote, or making a purchase.
ii. Purchase Behavioral Targeting
Use this type to track purchase histories and past transactions to understand consumer behavior. You can monitor:
- What they buy
- How often they reorder
- What combinations they choose
With that, you can display relevant ads and offers tailored to your existing customers. Whether it is a repeat purchase reminder or a cross-sell for related products, this approach makes each advertising campaign more effective in turning new-time buyers into repeat customers.
For example, if someone purchases an ergonomic office chair, you can target them based on that behavior and show ads for matching standing desks, monitor arms, or discounted office accessories. This keeps your offer relevant and encourages a larger order.
iii. Network Behavioral Targeting
Network targeting follows users on a particular website or even across other websites. It creates a broader picture of user interests and behaviors beyond your site.
Think of it like this: You get to know your audience without them ever filling out a form. That is what this approach does. It uses cookies and tracking pixels to connect the dots across their browsing habits.
Let’s say someone visits automotive blogs, browses sports updates, and reads business news. Together, that signals they might be a car-savvy professional.
Even without searching for cars, ad networks leverage that pattern to show vehicle ads across different websites they visit. It is targeted, and it travels with them.
iv. Time-Based Behavioral Targeting
It is not just about what people do; it is about when they do it. Timing reveals patterns that help you reach the right person at the right moment. When you target customers based on time, your marketing efforts become sharper and more strategic.
For example, suppose you are in the real estate space offering these cost segregation services to property investors. You will likely see traffic spike during business hours when they are actively managing finances or planning tax strategies.
That is the ideal time to show relevant ads featuring free consultations, limited-time tax savings, or case studies tailored to commercial property owners.
But if you are selling YouTube editing services to content creators, they often browse late at night or on weekends, once they finish filming. That is your sweet spot for showing offers on editing packages or turnaround guarantees.
v. Search Behavioral Targeting
Every time someone enters a phrase into a search engine, they reveal what is on their mind. Search behavioral targeting uses those search queries to understand what people are actively looking for.
These keywords give insight into real intent: what they want, need, or plan to do next. It helps you align your message with what is already top of mind.
For example, if someone searches for “best CRM for startups,” your online advertising campaign can show them a tailored ad for your CRM platform with startup-specific features.
Inside The Playbook: 3 Behavioral Targeting Moves from Industry Giants
Read these behavioral targeting examples, highlight the tactics from each brand, and jot down how you can apply them to your strategy.
A. Amazon
Amazon uses advanced behavioral targeting techniques to track every product view, purchase, and scroll to understand each user’s interests. That is how it nails ad targeting and personalized offers.
Those “Frequently Bought Together” and “Customers Who Bought This Also Bought” sections? They are driven by deep data collection and analysis of customer behavior from millions of similar shoppers.

What can your brand learn?
- Personalize without creeping people out. Focus on being helpful, not pushy.
- Pair products strategically and bundle items based on real buying patterns
- Serve content that evolves. Adjust homepage, ads, or emails based on fresh behavior.
Amazon proves relevance wins. Use these tactics to turn interest into action.
B. Airbnb
Airbnb turns behavioral advertising into a seamless user experience. It watches every click, filter, and booking to understand the user’s behavior, then responds with smart website personalization.
For example, if a user filters for beachfront homes, adds a few coastal listings to their wishlist, and books a summer stay, Airbnb takes note and creates a preference profile that improves future recommendations.
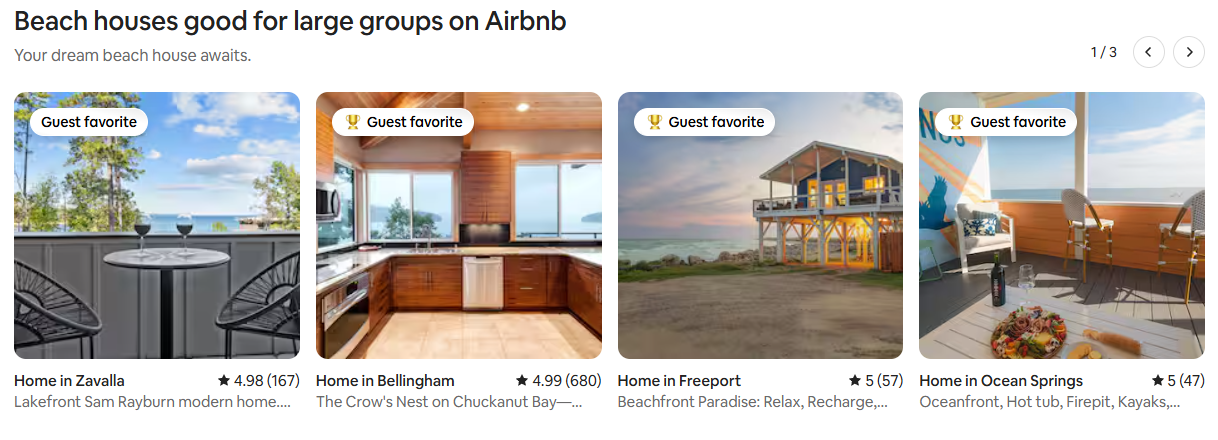
The next time they browse, the platform highlights similar beachfront stays, shows travel dates aligned with school holidays, and surfaces listings with outdoor dining or ocean views. It makes behavioral advertising feel less like a pitch and more like a helpful nudge.
Here’s what other brands can take away:
- Shape each user segment around goals. In this instance, family trips vs. solo adventures need different recommendations.
- Use filters as intent signals. Treat them as gold for targeting, not just search tools.
- Create dynamic product displays that shift based on what a user clicked or saved, not just general popularity.
Airbnb shows relevance builds results, behavior makes that possible.
C. Netflix
Netflix does not just recommend what is trending, it curates a homepage that feels made for you. Through smart behavioral marketing, it tracks what you watch, pause, skip, or binge across devices.

It then adjusts categories, thumbnails, and suggestions in real time. You can see “Because You Watched…” or a totally different cover image for the same show. It is all designed to keep you watching longer.
Here’s what you can learn:
- Design personalized experiences across devices, especially mobile apps, where most users scroll fast.
- Build behavior-based categories that reflect mood, timing, or habits, not just product type.
- Refresh content without overwhelming. Netflix rotates what shows up first, even if the content has not changed. You can do the same with product placements or featured offers.
Watch, learn, adapt. That is the Netflix playbook.
Ready To Get Personal? Here’s How To Do Behavioral Targeting Right
Follow each step closely and apply it to build an effective behavioral targeting strategy that meets your audience at the right moment, with the right message that moves them to act.
Step 1: Lay The Groundwork With Smart Data Collection
Before you jump into campaigns or try to tailor ads, pause and ask yourself:
- Do you actually know what your audience does, or are you just assuming?
You need to catch the real signals, like what people click, where they hesitate, and what makes them bounce, so you can deliver highly relevant ads that feel spot-on, not generic.
Smart data collection is how you turn guesswork into clarity. It connects the dots between what people explore and what they are ready to act on. Skip this step, and you are just shouting into the void.
What To Do
Install behavior trackers on your online store to see what users click, ignore, or abandon. To do this, use Google Tag Manager (GTM) to easily add and manage tracking tags across your site, without needing to update your code every time.
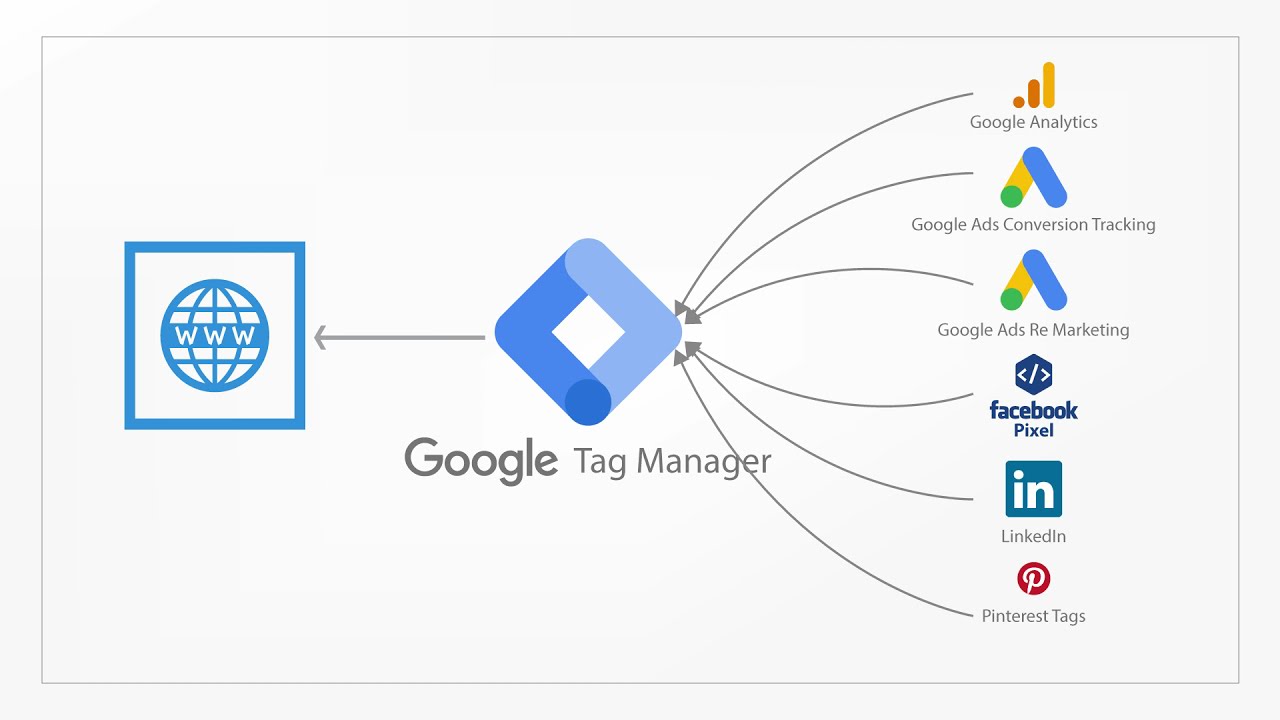
Setting this up can get technical, so bring in a developer or someone who knows Google Tag Manager well. Then, you can use Google Analytics to track customer behavior flows, like this:
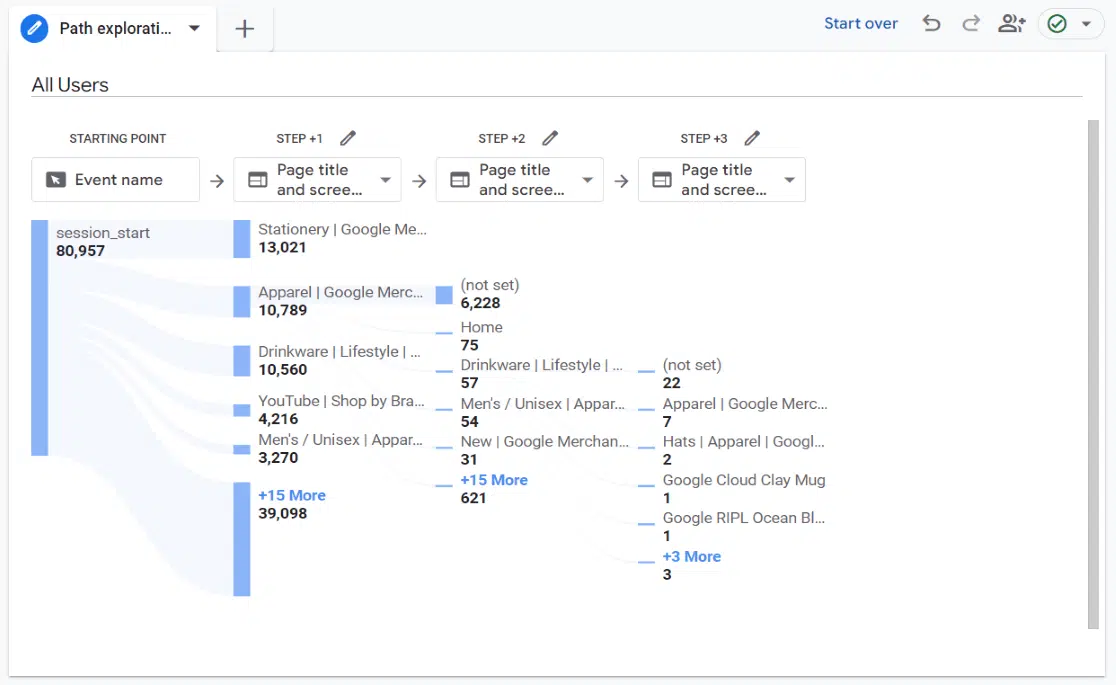
Here are more ways to collect data:
- Collect first-party data through forms, surveys, or signups. Offer something valuable, like a discount or lead magnet, in exchange for info.
- Use third-party data to fill in the gaps. You can buy them to enrich your customer profiles, but make sure they align with your existing insights.
- Analyze email and campaign engagement and check what people open, click, or skip. These patterns show what topics or offers move them.
To make collecting data easier, make your website trustworthy, starting with something as simple as your domain. Use a clean, professional domain extension to help your brand look more credible at first glance.
When visitors feel safe, they are more likely to engage, sign up, and share information, giving you better data to fuel your behavioral targeting efforts.
But make sure you and your team read up on data privacy laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
Step 2: Find The Patterns, Build The Right Groups
Now that you have the data, it is time to spot the patterns and create user segments that reflect how people behave. You need to group users based on shared actions so you can send targeted messages that feel personalized and timely.
The goal? Move from generic ad campaigns to marketing that speaks directly to intent.
What To Do
Segment by browsing behavior. To do this, group your visitors who explore similar product categories or features. For example, suppose you are in the B2B niche running a platform like Business For Sale, which lets entrepreneurs buy and sell businesses.
If a visitor spends time browsing listings for cafes and restaurants, group them into a behavioral segmentation category focused on hospitality. Then, show them targeted messages like “Top 10 Cafes for Sale in Sydney Right Now” or advice for buying food-based businesses. These are content and ad campaigns that match what they are interested in.
In addition, use past purchase behavior. Track what someone bought, how often, or what they skipped. Then build specific groups around high-value buyers, first-timers, or cart abandoners.
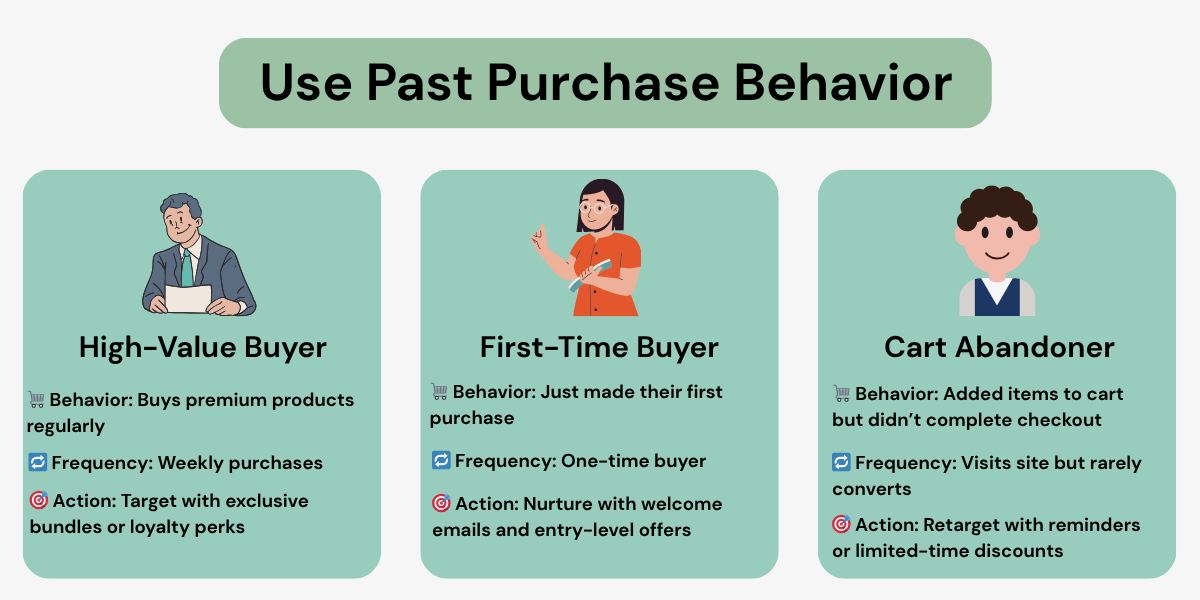
Another segmentation tactic is to combine your demographic data, like location or age, with behavioral patterns. Going back to our example, let’s say a user based in Sydney regularly browses transport and logistics business listings.
By combining their demographic data (location) with this behavioral pattern, you can create a user segment and deliver tailored messages like “Top Logistics Businesses for Sale in Sydney” or location-specific buying guides.
Step 3: Speak Their Language, Show What Matters
You have grouped your audience; now it is time to speak their language. This is where things get personal.
Use what you learned from their behavior to deliver personalized messaging that feels helpful, not salesy. But think beyond surface-level interests. Tap into their journey, like the clicks, the pauses, the paths they take, and match your message to their moment.
That is how great behavioral targeting campaigns work. They do not interrupt, they guide. With this step, you can lead with relevant ad experiences that make people feel understood and ready to act.
What To Do
- Personalize your emails. Include product names, categories browsed, or services viewed.
- Pull past activity into your follow-ups. It is an easy way to show a relevant ad that feels familiar.
- Match offers to behavior triggers. For example, send a discount or freebie based on what someone clicked or abandoned.
- Use dynamic copy in your ads. Write versions of your message that change based on user behavior.
If you are juggling a bunch of campaigns, do not be afraid to let AI tools help you write faster because it makes content and ads way easier to manage. Just do not let it sound like a robot wrote it. Add a human touch, keep it natural, and make sure it still speaks to what your audience actually cares about, because that is the heart of behavioral targeting.
Nail Your Strategy: Behavioral Targeting Dos & Don’ts
Behavioral targeting can increase conversion rates and build brand loyalty, but only if you use it with intention. There is a fine line between helpful and annoying in digital advertising, and crossing it can cost you trust.
These dos and don’ts help you stay on track, so your targeting feels smart, not spammy.
The Dos
- Keep a shared record of who you are targeting, why, and what you expect to happen.
- Align behavioral goals with business outcomes. For example, tie targeting efforts to revenue, retention, or lifetime value.
- Build a clear data-to-decision workflow to make sure your team knows how behavior turns into messaging, not just where data lives.
- Coordinate between marketing, product, and sales to make sure insights and timing are in sync.
The Don’ts
- Do not chase personalization at the expense of privacy. If it feels invasive, it backfires.
- Do not forget mobile behavior because it often tells a different story from desktop.
- Do not let old behaviors define new strategies. Behavior shifts fast, so should your targeting playbook.
- Do not isolate behavioral data from other insights. Blend it with surveys, feedback, and support data to see the full picture.
Conclusion
Start small. Review your current ad campaigns and flag where behavioral targeting can sharpen relevance. Then, gather your team and map out one high-intent segment, like cart abandoners or active browsers, and build around it.
Test one message, tailor one offer, and measure what shifts. Take one step today that brings you closer to smarter, more profitable marketing.
Ready to act?
Start with trust. Partner with ShortDot and use a secure, memorable domain extension that builds credibility from the first click and makes collecting data feel safe and natural. Reach out now to know more.
Author Bio:

Burkhard Berger is the founder of Novum™. He helps innovative B2B companies implement modern SEO strategies to scale their organic traffic to 1,000,000+ visitors per month. Curious about what your true traffic potential is?
Gravatar: vip@novumhq.com
